In the era of data-driven business decisions, services such as web scraping, data extraction and data mining have become integral tools for companies seeking to use data for competitive advantage such as in case of market research or price monitoring.
However, the in-house web scraping operation comes with a number of challenges that consume company resources, lower data quality, and increase organizational risk.
For B2B companies, these issues are critical when formulating a lasting data strategy.
In this article, we’ll break down the five challenges of in-house web scraping and share with you the information you need to take control of data acquisition without making expensive errors.
Why In-House Web Scraping Poses Challenges?
Web scraping provides businesses with necessary tools to obtain structured business data from various online platforms, which helps drive value-adding business decisions such as inventory optimization and competitor analysis.
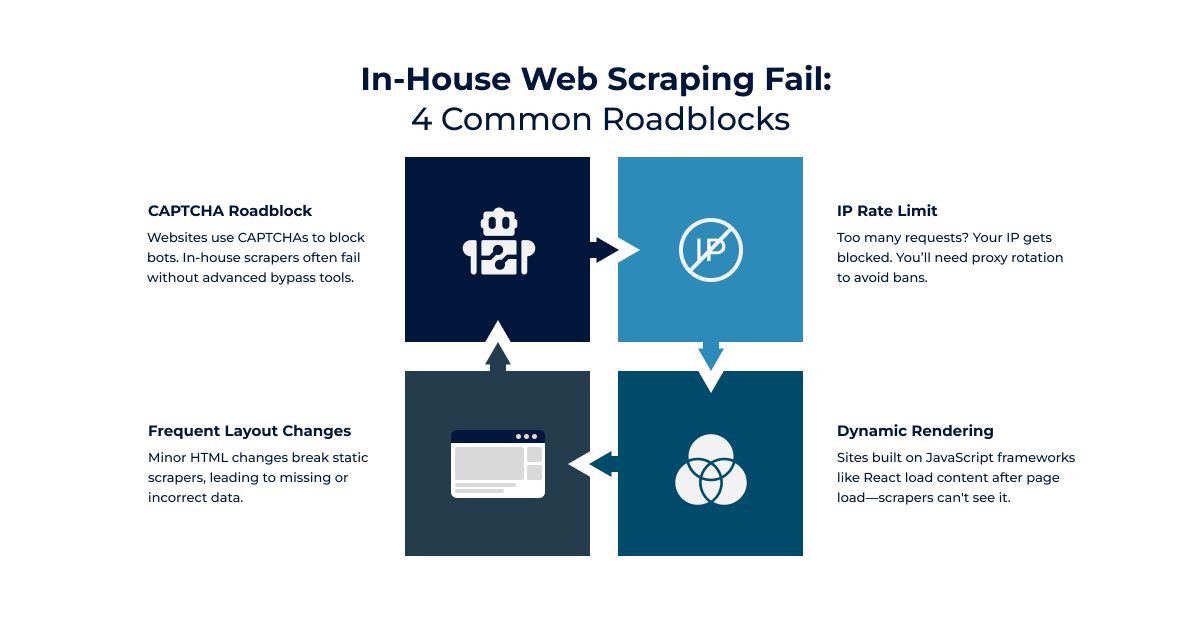
However, as a result of the growing technology, modern websites employ various anti-scraping techniques such as CAPTCHAs, IP rate limiting, and dynamic rendering which increase the complexity for in-house efforts.
Under such conditions, businesses are bound to experience lead to wasted company resources, inconsistencies in data, and legal challenges. Through these challenges, we hope to provide B2B teams with dependable scraping strategies that ultimately augment business growth.
Pitfall 1: Infrastructure Complexity and Maintenance Overheads
The Challenge
Building a web scraping infrastructure is an expensive and time-consuming undertaking requiring software, hardware, and technical expertise.
For in-house teams, managing the proxy network for IP rotation, setting servers for uptime, and adapting scrapers to handle DOM changes, CAPTCHA bots, or scrub-anti-bot measures on a routine basis means scrapers need constant maintenance.
This need for maintenance is a new hurdle, and for weeks or months, adapting to defenses or layout changes is a drain on resources. JavaScript frameworks like React dynamically render content which means scrapers need constant adjustment and maintenance.
Best Practices
Adopt Modular Design: Scraping scripts are easier to maintain if they are built using separate modules like data parsing and proxy handling that can change independently.
Leverage Open-Source Tools: Use frameworks like Beautiful Soup for flexible crawling, paired with headless browsers like Puppeteer for JavaScript rendering, reducing dependency on custom infrastructure.
Implement Automated Monitoring: Set up real-time alerts and log analysis to detect failures (e.g., IP bans or missing data), enabling proactive maintenance before issues escalate.
Optimize Resource Use: Schedule scraping for off-peak traffic times and employ lightweight proxies to lessen server strain, improving efficiency and saving money.
Pitfall 2: Legal and Compliance Risks
The Challenge
Website scraping is done in a legal grey area. It is controlled by a set of guidelines and regulations such as GDPR, CCPA and a sites Terms of Service (ToS). In-house teams may unintentionally overload servers with excessive requests or collect personal data without consent, risking fines or reputational damage.
For example, overly aggressive scraping without employing rate-limiting may violate ToS and result in data breaches which may lead to high-profile legal repercussions for the companies involved.
Best Practices
Respect Rate-Limit and ToS: Enforce compliance with request throttling (e.g. requests-per-minute caps) and honor robots.txt directives to align with website policies.
Anonymize Data Collection: With regards to privacy laws, filter out Personally Identifiable Information (PII) through data masking techniques to PII compliance.
Maintain Audit Trails: As part of compliance, log scraping timestamps, IP addresses, and data field collection, and secure storage to demonstrate compliance during audits.
Engage Legal Counsel: Scraping policy should be regularly and proactively reviewed with legal counsels to guarantee compliance with the borderless legislation.

Pitfall 3: Data Quality and Consistency Issues
The Issue
In-house web scraping is prone to inconsistencies because of incomplete and systematically unfinished datasets. Additionally, the website layout changes such as product pages that update the locations of their price fields can render static selectors useless, causing critical data to be missed or rendered inaccurately.
Data-quality issues due to scraping are so prevalent that businesses are increasingly unable to make sound historical analyses affecting pricing and inventory decisions.
Best Practices
Use Adaptive Parsing Logic: To reduce scraping breakage, design flexibly framed parsers that utilize regex or XPath with wildcards, soft selectors, or equip scrapers with algorithms that handle adaptive processing.
Implement Data Validation: Post-scraping verification checks should be carried out to ensure all critical data fields are populated (e.g., price and availability) and flag counterfactuals for validation.
Standardize Output Formats: Maintain merged integration of datasets that utilize a common schema (e.g., JSON with designated fields) to eliminate discrepancies.
Test with Sample Data: Extracting data from a subset of target sites should be a routine practice for testing and robust refining of site scripts and their relevance within a broader context.
Pitfall 4: Scalability Bottlenecks
The Challenge
Typically, in-house scraping systems struggle to handle a large amount of data or multiple sites simultaneously. With only a single-source scraper, scaling up to hundreds of sources would require the implementation of additional proxies, servers, as well as bandwidth, which is far from instant.
To make things worse, IP bans and dynamic content as well as other anti-scraping measures make scaling a lot harder, which is an issue for data that is time sensitive, especially during critical periods like market expansions.
Best Practices
Design Distributed Systems: Use cloud-based architectures with load balancers to distribute scraping tasks across multiple nodes, improving capacity and resilience.
Implement Parallel Crawling: Set up page or site per script concurrent processing to take advantage of concurrent request tools that will aid in throughput.
Utilize Proxy Rotation: Deploy a diverse proxy pool with automated rotation to avoid bans, ensuring continuous access as request volume grows.
Plan for Growth: Start with a scalable framework (e.g., Docker containers for easy scaling) and test under increasing loads to identify bottlenecks early.
Pitfall 5: Talent Acquisition and Retention Challenges
The Challenge
The process of building an in-house scraping team requires several specific roles such as data engineers, web developers, and compliance experts. These roles are scarce internationally.
Acquiring and maintaining skilled strategists, be it in proxy management or anti-bot evasion, proves challenging which leads to either stalled project because of in-house staffing limitations, or a dependency on underqualified personnel.
This absence of expertise can create brittle systems that do not efficiently process and analyze the data undergo system overload, stalling data driven projects.
Best Practices
Invest in Training: Upskill existing developers with online courses or workshops on scraping tools (e.g., Selenium, BeautifulSoup) and compliance best practices.
Leverage Community Resources: Tap into open-source communities for support, using forums or GitHub to troubleshoot issues and adopt proven codebases.
Document Processes: By providing written documentation on the scraping tasks, a person’s dependency on other experts diminishes thereby helping in knowledge transfer.
Outsource Non-Core Tasks: Focus on strategic projects can be achieved by assigning the repetitive tasks to external specialists such as controlling the regularly scheduled tasks for upkeep or setting up the intricate ones.
Conclusion:
Conducting web scraping in-house offers some level of control, but there are significant challenges such as legal issues, overly complex infrastructure, data quality, troubles with scalability, lack of talent, and legal issues.
These challenges could sabotage data strategies, in turn wasting valuable time, resources, and sinking the organization’s credibility.
Following best practices such as modular design, compliance, adaptive parsing, distributed systems, team building, and others, overcome these challenges and fully harness the power of web scraping.
Partner with RDS Data
Overcoming scraping challenges demands high levels of expertise and constant effort, which can easily exhaust internal teams. At RDS Data, we have tailored compliant B2B scraping solutions at scale, and mastered the challenge of compliance and reliability through years of industry-focused mastered challenges.
Don’t let in-house web scraping sabotage data strategies. Partner with RDS Data and transform data acquisition strategies into competitive advantages.
Want to avoid pitfalls the in-house web scraping issues while keeping the team and resources?
Book a free consultation and let us put years of experience with B2B data to use for you. Contact us today.
Tired of broken scrapers and messy data?
Let us handle the complexity while you focus on insights.

